Accumulator is installed in hydraulic systems with the idea of conserving or storing energy and smoothening pulsations as efficiently as possible. These are energy-storing devices. They are quite similar to rechargeable batteries that are used in electrical systems. These store and release energy in the form of pressurized fluids and are widely used to improve hydraulic system's efficiency.
Accumulator is a pressure vessel that keeps compressed gas (nitrogen) and compressed hydraulic fluid. The shell or wall of this vessel is formulated of stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, and reinforced fiber composites. There is a flexible barrier internally to separate the compressed gas or hydraulic fluid.
Accumulator are used in hydraulic circuits, allowing us to select pumps lower than the maximum HP required. There are many types of hydraulic accumulators available.
Looking forward to knowing more about accumulators, read this article till the end!
Operating States of Hydraulic Accumulators
Accumulators use the compressibility of nitrogen gas, providing better energy efficiency, deafening noises, and maximizing safety.
Integrating or combining an accumulator with a piece of hydraulic equipment or any other machinery that uses fluids can be triggered to start accumulating pressure. This can temporarily supply greater fluids or help absorb vibrations or any impact from pipes.
It can also sink in, uplifting the overall performance of any equipment or machinery working with the system. It also promises energy efficiency and silent operation.
The following will help you understand the structure and operation states of a bladder type of accumulator.
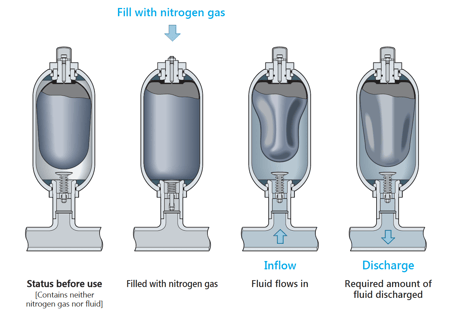
Types of Hydraulic Accumulators
Hydraulic accumulators come in three different types, each with its own function.

1. Piston Accumulator
The piston accumulator appears like a hydraulic cylinder, just without a rod. And like most accumulators, a piston accumulator comes with the same elements such as gas section, fluid section, and piston used to separate the two sections. This accumulator is a staple for large stored volumes such as 100 gallons or more.
The emulators do have a high and strong flow. The pressure entirely depends on the size of the accumulator, but one should never try to use a piston accumulator for shock applications. The piston accumulators are designed for heavy-duty or rugged applications. But, these are much more sensitive or prone to the contamination that can harm the seals. And it is also a fact that one can easily fix the accumulator by fixing the piston seals.
2. Bladder Accumulator
A bladder accumulator with large ports promotes easy fluid discharge and ensures your device stays safe from all sorts of dirt and contamination. This accumulator is always mounted or installed vertically and sometimes horizontally in low-cycle applications.
These bladder-type accumulators are designed with an excellent notion to have a pressure ratio of 4:1, just to protect the bladder from any sort of material distortion and strain. Professionals believe that bladder accumulators are the very best when it comes to general-purpose units. And these are available in a vast range of sizes. Their good response characteristics make them the best suited for shock application.
3. Diaphragm Accumulator
A diaphragm accumulators work much like the bladder accumulators. The key difference between a bladder accumulator and a diaphragm accumulator is that the former accumulator uses an elastic diaphragm instead of a rubber bladder. The elastic diaphragm is used to separate the gas and oil sections. The best thing about these accumulators is that they are lightweight, compact, and economical devices that give out small flow and volume.
This accumulator can handle a greater compression or pressure ratio, typically from 8:1 to 10:1 , as a rubber barrier will not distort to the same degree as a rubber bladder. Not just this, diaphragm accumulators also provide better mounting flexibility and are not that typically sensitive to contamination. Also, this type of accumulator will react much faster to pressure changes. This is why the diaphragm accumulators are best for shock applications.
Functions of an Accumulator
1. Energy Accumulation
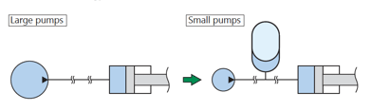
Accumulators are widely used as a supplementary energy source. The system in which pressurized oil discharged from accumulators is used to operate cylinders enables pumps to be smaller, shortens their cycles, and conserves energy.
2. Pulse Absorption
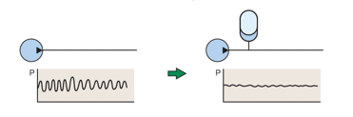
All pressurized fluid discharged from pumps has a pulse. Pulses produce noise or vibrations that can cause instability or damage devices. The use of an accumulator can attenuate pulses.
3. Impact Absorption
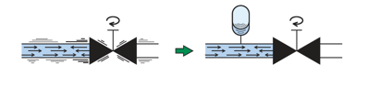
The rapid closure of valves or sudden changes in load within a hydraulic circuit can result in impact pressure in pipes, which can then lead to noise or damage to those pipes or devices. The use of an accumulator can mitigate any such internal shock.
4. Thermal Expansion Compensation
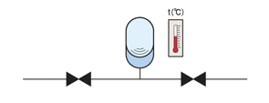
Changes in the volume of a liquid resulting from changes in the temperature within a closed circuit can increase the internal pressure. An accumulator can be used to mitigate any such fluctuations in the pressure.
Major Examples of Usage
1. Hydraulic presses
- Injection molding machines
- Die-cast machines
- Automotive brake systems
- Power shovels
- Vibration testing machines
- Circuit breakers for transformer substations
- Water supply systems
- Home pumps
- Equipment for ironworks, power plants, and chemical plants
- Ship engines
2. Machine tools
- Breakers for construction machinery
- Concrete compressors
- Hydraulic elevators
- Power sprayers
- Water purification plants
- Descaling equipment
3. Water pipes
- Jet fuel injection equipment
- Mud-water compressors
- Pipelines
4. Boilers
- Pressurized water heaters
- Central heating systems
- Fire extinguishing systems
Use of Accumulators in the Construction Machinery Industry
1. Wheel loader / Excavator: Pilot Circuit
 Equipping the pilot circuit with a hydraulic accumulator can release the excess hydraulic pressure from the circuit. The MUV and MU types are majorly used in pilot circuits. These are not that costly and do not have a gas valve. But you can still measure the residual gas pressure through inflection point measurement.
Equipping the pilot circuit with a hydraulic accumulator can release the excess hydraulic pressure from the circuit. The MUV and MU types are majorly used in pilot circuits. These are not that costly and do not have a gas valve. But you can still measure the residual gas pressure through inflection point measurement.
2. Excavator: Breaker
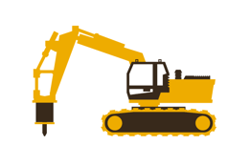 The effect of hydraulic pressure from the accumulator sinks in improving the striking piston speed depends on the type of circuit breaker used. Furthermore, accumulators absorb all sorts of hydraulic vibrations or pulsations, especially while using the breaker. It successfully suppresses all the load on the hydraulic equipment and extends the usable life of the related equipment.
The effect of hydraulic pressure from the accumulator sinks in improving the striking piston speed depends on the type of circuit breaker used. Furthermore, accumulators absorb all sorts of hydraulic vibrations or pulsations, especially while using the breaker. It successfully suppresses all the load on the hydraulic equipment and extends the usable life of the related equipment.
3. Wheel Loader
 An accumulator is known because of its ability to significantly reduce low-frequency vibrations like bouncing and pitching, which are often caused by uneven surfaces of the roads. An accumulator helps you achieve incredible driving performance and reduces operator fatigue to a great extent. The vehicle speed sensor and controller operate the accumulator, showcasing optimum pulsation suppression. It is triggered automatically as the speed increases and automatically turns off when driving at a slower speed. Hence, it keeps you from hassle switching operations.
An accumulator is known because of its ability to significantly reduce low-frequency vibrations like bouncing and pitching, which are often caused by uneven surfaces of the roads. An accumulator helps you achieve incredible driving performance and reduces operator fatigue to a great extent. The vehicle speed sensor and controller operate the accumulator, showcasing optimum pulsation suppression. It is triggered automatically as the speed increases and automatically turns off when driving at a slower speed. Hence, it keeps you from hassle switching operations.
4. Rough Terrain Crane / Dump Truck: Suspension When you embrace a piston-type accumulator for your hydro-pneumatic suspension circuit, it lets you drive your vehicle with better control, comfortability, and smoothly even on uneven roads.
When you embrace a piston-type accumulator for your hydro-pneumatic suspension circuit, it lets you drive your vehicle with better control, comfortability, and smoothly even on uneven roads.
5. Pile Machine Due to the change of hydraulic fluid in the clamp part of the closed circuit, pressure will continue to fluctuate. To reduce such changes or pressure fluctuations, it is advised to use a hydraulic accumulator.
Due to the change of hydraulic fluid in the clamp part of the closed circuit, pressure will continue to fluctuate. To reduce such changes or pressure fluctuations, it is advised to use a hydraulic accumulator.
6. Forklift: Accumulator for Shock Absorption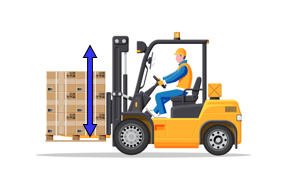 Using an accumulator will help your vehicle absorb shocks and vibrations from any type of road surface. Not just this, it also reduces the overall burden on the operator, heightens safety, boosts work efficiency, and cuts off unnecessary and unwanted noise!
Using an accumulator will help your vehicle absorb shocks and vibrations from any type of road surface. Not just this, it also reduces the overall burden on the operator, heightens safety, boosts work efficiency, and cuts off unnecessary and unwanted noise!
7. Forklift: Brake Assist Accumulator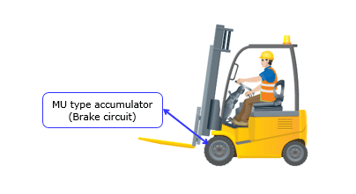 The amount of hydraulic pressure that the accumulator stores can also be used in the brake circuit to maximize the vehicle's braking power. Not just this, this can also be used to nullify the fluctuations in the braking distance caused by the loads. Again, there are perks of using a low gas porous material with standard low-temperature flexibility for the bladder. It can be used as a freezer or refrigerator and even used outdoors at room temperature.
The amount of hydraulic pressure that the accumulator stores can also be used in the brake circuit to maximize the vehicle's braking power. Not just this, this can also be used to nullify the fluctuations in the braking distance caused by the loads. Again, there are perks of using a low gas porous material with standard low-temperature flexibility for the bladder. It can be used as a freezer or refrigerator and even used outdoors at room temperature.
Conclusion
Now that you have read this article here, I hope this article has helped you find the answer you were looking for! As you have read, accumulators act as storage units and store energy! The reserved energy is used in supplementing the primary system if there is an emergency or lack of power.
Besides that, the accumulator greatly improves your hydraulic system, develops response time, and cuts off unwanted pulsations, shocks, vibrations, and so forth! All in all, accumulators keep your hydraulic system free of contamination and perfectly usable!
About NOK
NOK Accumulators have proved very popular with many customers as they are highly reliable with a wide-ranging lineup supported by global top-class rubber materials, seals, and processing techniques, were designed with the environment taken into consideration, and are ISO14000 compliant.
Contact us now for more info regarding accumulator at contact.us@slsbearings.com.sg or simply click on below button to send us your enquiries.







